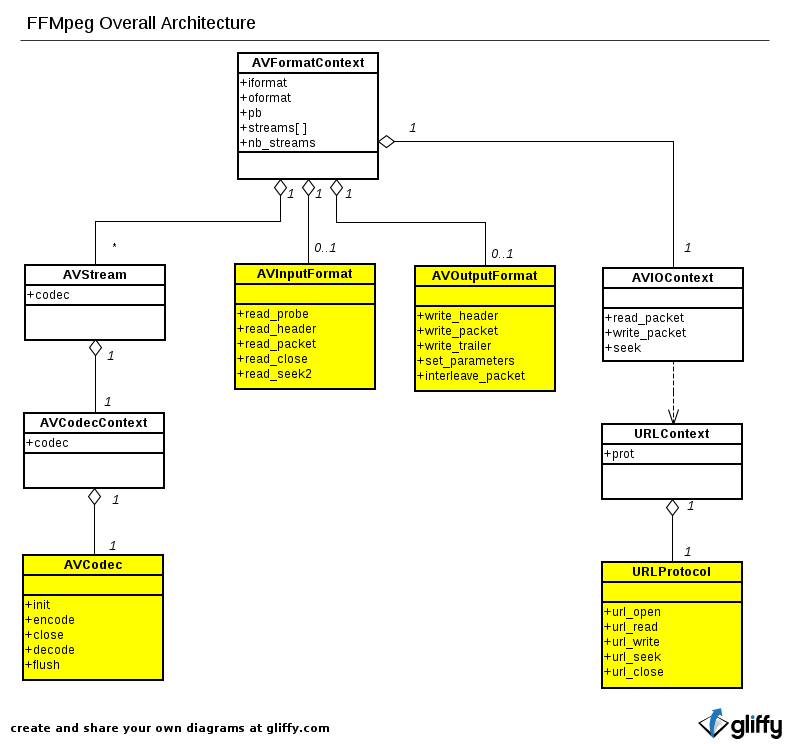
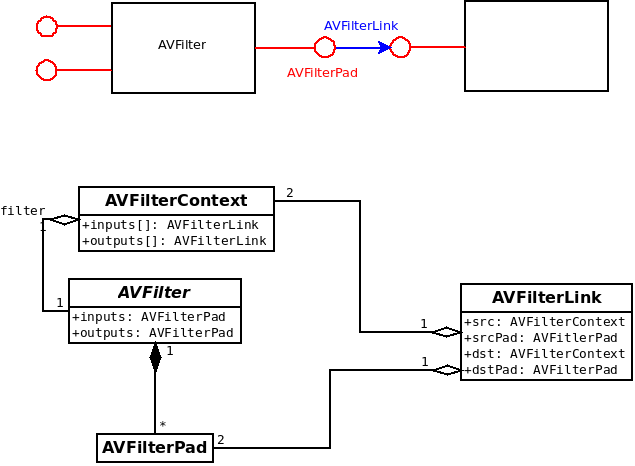
根据多处转载的记录,原文最早追溯写于2012年12月,部分来源与出处已经访问不到,老马这里把各处的信息,整理做一个完整版的备份,供查阅及参考使用。
认识FFMPEG
FFMPEG堪称自由软件中最完备的一套多媒体支持库,它几乎实现了所有当下常见的数据封装格式、多媒体传输协议以及音视频编解码器,堪称多媒体业界的瑞士军刀。因此,对于从事多媒体技术开发的工程师来说,深入研究FFMPEG成为一门必不可少的工作,可以这样说,FFMPEG之于多媒体开发工程师的重要性正如kernel之于嵌入式系统工程师一般。
几个小知识:
- FFMPEG项目是由法国人Fabrice Bellard发起的,此人也是著名的CPU模拟器项目QEMU的发起者,同时还是圆周率算法纪录的保持者。
- FF是Fast Forward的意思,翻译成中文是“快进”。
- FFMPEG的LOGO是一个”Z字扫描”示意图,Z字扫描用于将图像的二维频域数据一维化,同时保证了一维化的数据具备良好的统计特性,从而提高其后要进行的一维熵编码的效率。
关于耻辱厅(Hall of Shame):FFMPEG大部分代码遵循LGPL许可证,如果使用者对FFMpeg进行了修改,要求公布修改的源代码;有少部分代码遵循GPL许可证,要求使用者同时公开使用FFMpeg的软件的源代码。实际上,除去部分具备系统软件开发能力的大型公司(Microsoft、Apple等)以及某些著名的音视频技术提供商(Divx、Real等)提供的自有播放器之外,绝大部分第三方开发的播放器都离不开FFMpeg的支持,像Linux桌面环境中的开源播放器VLC、MPlayer,Windows下的KMPlayer、暴风影音以及Android下几乎全部第三方播放器都是基于FFMPEG的。也有许多看似具备自主技术的播放器,其实也都不声不响地使用了FFMPEG,这种行为被称为“盗窃”,参与“盗窃”的公司则被请入耻辱厅,如于2009年上榜的国产播放器暴风影音、QQ影音。
关于FFMPEG的商业应用:与其他开源软件不同的是,FFMPEG所触及的多媒体编解码算法中有相当一部分处于大量的专利涵盖范围之内,因此,在商业软件中使用FFMPEG必须考虑可能造成的对专利所有者的权利侵犯,这一点在FFMPEG的官方网站也有所提及,所涉及的风险需使用者自行评估应对。
FFMPEG从功能上划分为几个模块,分别为核心工具(libutils)、媒体格式(libavformat)、编解码(libavcodec)、设备(libavdevice)和后处理(libavfilter, libswscale, libpostproc),分别负责提供公用的功能函数、实现多媒体文件的读包和写包、完成音视频的编解码、管理音视频设备的操作以及进行音视频后处理。
使用FFMPEG
这里指FFMPEG提供的命令行(CLI)工具ffmpeg,其使用方法如下(方括号表示可选项,花括号表示必选项目):
ffmpeg [global options] {[infile options]['-i' 'infile'] ...} {[outfile options] 'outfile' ...}
参数选项由三部分组成:可选的一组全局参数、一组或多组输入文件参数、一组或多组输出文件参数,其中,每组输入文件参数以‘-i’为结束标记;每组输出文件参数以输出文件名为结束标记。
基本选项
能力集列表
- -formats:列出支持的文件格式。
- -codecs:列出支持的编解码器。
- -decoders:列出支持的解码器。
- -encoders:列出支持的编码器。
- -protocols:列出支持的协议。
- -bsfs:列出支持的比特流过滤器。
- -filters:列出支持的滤镜。
- -pix_fmts:列出支持的图像采样格式。
- -sample_fmts:列出支持的声音采样格式。
常用输入选项
- -i filename:指定输入文件名。
- -f fmt:强制设定文件格式,需使用能力集列表中的名称(缺省是根据扩展名选择的)。
- -ss hh:mm:ss[.xxx]:设定输入文件的起始时间点,启动后将跳转到此时间点然后开始读取数据。
对于输入,以下选项通常是自动识别的,但也可以强制设定。
- -c codec:指定解码器,需使用能力集列表中的名称。
- -acodec codec:指定声音的解码器,需使用能力集列表中的名称。
- -vcodec codec:指定视频的解码器,需使用能力集列表中的名称。
- -b:v bitrate:设定视频流的比特率,整数,单位bps。
- -r fps:设定视频流的帧率,整数,单位fps。
- -s WxH : 设定视频的画面大小。也可以通过挂载画面缩放滤镜实现。
- -pix_fmt format:设定视频流的图像格式(如RGB还是YUV)。
- -ar sample rate:设定音频流的采样率,整数,单位Hz。
- -ab bitrate:设定音频流的比特率,整数,单位bps。
- -ac channels:设置音频流的声道数目。
常用输出选项
- -f fmt:强制设定文件格式,需使用能力集列表中的名称(缺省是根据扩展名选择的)。
- -c codec:指定编码器,需使用能力集列表中的名称(编码器设定为”copy“表示不进行编解码)。
- -acodec codec:指定声音的编码器,需使用能力集列表中的名称(编码器设定为”copy“表示不进行编解码)。
- -vcodec codec:指定视频的编码器,需使用能力集列表中的名称(编解码器设定为”copy“表示不进行编解码)。
- -r fps:设定视频编码器的帧率,整数,单位fps。
- -pix_fmt format:设置视频编码器使用的图像格式(如RGB还是YUV)。
- -ar sample rate:设定音频编码器的采样率,整数,单位Hz。
- -b bitrate:设定音视频编码器输出的比特率,整数,单位bps。
- -ab bitrate:设定音频编码器输出的比特率,整数,单位bps。
- -ac channels:设置音频编码器的声道数目。
- -an 忽略任何音频流。
- -vn 忽略任何视频流。
- -t hh:mm:ss[.xxx]:设定输出文件的时间长度。
- -to hh:mm:ss[.xxx]:如果没有设定输出文件的时间长度的画可以设定终止时间点。
流标识
FFMPEG的某些选项可以对一个特定的媒体流起作用,这种情况下需要在选项后面增加一个流标识。流标识允许以下几种格式:
- 流序号。譬如“:1”表示第二个流。
- 流类型。譬如“:a“表示音频流,流类型可以和流序号合并使用,譬如“:a:1”表示第二个音频流。
- 节目。节目和流序号可以合并使用。
- 流标识。流标识是一个内部标识号。
假如要设定第二个音频流为copy,则需要指定-codec:a:1 copy
音频选项
- -aframes:等价于frames:a,输出选项,用于指定输出的音频帧数目。
- -aq:等价于q:a,老版本为qscale:a,用于设定音频质量。
- -atag:等价于tag:a,用于设定音频流的标签。
- -af:等价于filter:a,用于设定一个声音的后处理过滤链,其参数为一个描述声音后处理链的字符串。
视频选项
- -vframes:等价于frames:v,输出选项,用于指定输出的视频帧数目。
- -aspect:设置宽高比,如4:3、16:9、1.3333、1.7777等。
- -bits_per_raw_sample:设置每个像素点的比特数。
- -vstats:产生video统计信息。
- -vf:等价于filter:v,用于设定一个图像的后处理过滤链,其参数为一个描述图像后处理链的字符串。
- -vtag:等价于tag:v,用于设定视频流的标签。
- -force_fps:强制设定视频帧率。
- -force_key_frames:显式控制关键帧的插入,参数为字符串,可以是一个时间戳,也可以是一个“expr:”前缀的表达式。如“-force_key_frames 0:05:00”、“-force_key_frames expr:gte(t,n_forced*5)”
滤镜选项
高级选项
- -re:要求按照既定速率处理输入数据,这个速率即是输入文件的帧率。
- -map:指定输出文件的流映射关系。例如 “-map 1:0 -map 1:1”要求将第二个输入文件的第一个流和第二个流写入到输出文件。如果没有-map选项,ffmpeg采用缺省的映射关系。
用例
1、将一个老式的avi文件转成mp4
ffmpeg -i final.avi -acodec copy -vcodec copy final.mp4
2、从一个视频文件中抽取一帧图像:
ffmpeg -y -i test.mp4 -ss 00:03:22.000 -vframes 1 -an test.jpg
3
ffmpeg -i final.avi -vf scale=640:640 square.avi
4、使用alsa接口录制一段音频存放到某个wav文件中
ffmpeg -f alsa -i hw:0 -t 100 alsaout.wav
5、使用alsa接口搭建一个个人网络电台
ffmpeg -f alsa -i default -acodec aac -strict -2 -b:a 128k -r 44100 /var/www/data/main.m3u8
6、将一个mp4文件的音视频流实时转码之后发送给某个远程设备,远程设备可以通过http获取的sdp文件来接收rtp媒体数据。
ffmpeg -re -i example.mp4 -acodec copy -vcodec libx264 -s 480x270 -map 0:0 -f rtp rtp://10.131.202.62:1234 -map 0:1 -f rtp rtp://10.131.202.62:1238 > /var/www/live.sdp
编译和裁剪
FFMpeg与大部分GNU软件的编译方式类似,是通过configure脚本来实现编译前定制的。这种途径允许用户在编译前对软件进行裁剪,同时通过对宿主系统和目标系统的自动检测来筛选参与编译的模块并为其设定合适的配置。但是,FFMpeg的configure脚本并非如通常的GNU软件一样通过配置工具自动生成,而是完全由人工编写的。configure脚本生成的config.mak和config.h分别在Makefile和源代码的层次上实现编译的控制。
通过运行“./configure –help”可以了解到脚本支持的参数,这些参数大体分为下面几类:
- 标准选项——GNU软件例行配置项目如安装路径等。例:–prefix=…,……
- 列出当前源代码支持的能力集,如编解码器,解复用器,输入输出设备,文件系统等。例:–list-decoders,–list-encoders,……
- 授权选项:–enable-version3,–enable-gpl,–enable-nofree。代码的缺省授权是LGPL v2,如果要使用以LGPL v3、GPL授权的模块或者某些不遵循自有软件授权协议的模块,必须在运行configure时显式使能相应的选项。
- 编译、链接选项。例:–disable-static,–enable-shared,…… 缺省配置是生成静态库而不生成动态库,如果希望禁止静态库、生成动态库都需要显式指定。
- 可执行程序控制选项,决定是否生成ffmpeg、ffplay、ffprobe和ffserver。
- 模块控制选项,筛选参与编译的模块,包括整个库的筛选,例如:–disable-avdevice;一组模块的筛选,例如:–disable-decoders,单个模块的筛选,如:–disable-decoder=… 等。
- 专家级选项,允许开发者进行深度定制,如交叉编译环境的配置、自定义编译器参数的设定、指令级优化、debug控制等。
对于–disable、–enable类的控制选项,如果以–disable为前缀,则缺省是enable的,反之亦然。
总之,无论从商业角度还是技术角度出发,使用configure脚本对FFMpeg进行裁剪是最安全的方式,只有针对于某些configure无法满足的定制要求,才需要考虑修改configure脚本——甚至修改configure生成的配置文件。
以下是一个配置实例,实现运行与Android系统中的ffmpeg库的编译:
./configure --prefix=. --cross-prefix=$NDK_TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX --enable-cross-compile --arch=arm --target-os=linux --cpu=cortex-a8 \
--disable-static --enable-shared --enable-pic --disable-ffmpeg --disable-ffplay --disable-ffserver --disable-ffprobe \
--extra-cflags="-I$NDK_PLATFORM/usr/include" \
--extra-ldflags="-nostdlib -Wl,-T,$NDK_PREBUILT/arm-linux-androideabi/lib/ldscripts/armelf_linux_eabi.x \
-L$NDK_PLATFORM/usr/lib \
$NDK_PREBUILT/lib/gcc/arm-linux-androideabi/4.4.3/crtbegin.o $NDK_PREBUILT/lib/gcc/arm-linux-androideabi/4.4.3/crtend.o \
-lc -lm -ldl"
缺省的编译会生成4个可执行文件和9个库:可执行文件包括用于转码的ffmpeg、用于获取媒体信息的ffprobe、用于播放媒体的ffplay和用于推送媒体流的ffserver;库包括avutil、avformat、avcodec、avfilter、avdevice、swresample、swscale、postproc及avresample,其中,核心库有5个,分别为基础库avutil、文件格式及协议库avformat、编解码库avcodec、输入输出设备库avdevice和过滤器avfilter。
深入FFMPEG
示例程序
解码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "libavutil/avstring.h"
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
#include "libavdevice/avdevice.h"
#include "libavutil/opt.h"
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
#define DECODED_AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE 192000
struct options
{
int streamId;
int frames;
int nodec;
int bplay;
int thread_count;
int64_t lstart;
char finput[256];
char foutput1[256];
char foutput2[256];
};
int parse_options(struct options *opts, int argc, char** argv)
{
int optidx;
char *optstr;
if (argc < 2) return -1;
opts->streamId = -1;
opts->lstart = -1;
opts->frames = -1;
opts->foutput1[0] = 0;
opts->foutput2[0] = 0;
opts->nodec = 0;
opts->bplay = 0;
opts->thread_count = 0;
strcpy(opts->finput, argv[1]);
optidx = 2;
while (optidx < argc)
{
optstr = argv[optidx++];
if (*optstr++ != '-') return -1;
switch (*optstr++)
{
case 's': //< stream id
opts->streamId = atoi(optstr);
break;
case 'f': //< frames
opts->frames = atoi(optstr);
break;
case 'k': //< skipped
opts->lstart = atoll(optstr);
break;
case 'o': //< output
strcpy(opts->foutput1, optstr);
strcat(opts->foutput1, ".mpg");
strcpy(opts->foutput2, optstr);
strcat(opts->foutput2, ".raw");
break;
case 'n': //decoding and output options
if (strcmp("dec", optstr) == 0)
opts->nodec = 1;
break;
case 'p':
opts->bplay = 1;
break;
case 't':
opts->thread_count = atoi(optstr);
break;
default:
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
void show_help(char* program)
{
printf("Simple FFMPEG test program\n");
printf("Usage: %s inputfile [-sstreamid [-fframes] [-kskipped] [-ooutput_filename(without extension)] [-ndec] [-p] [-tthread_count]]\n",
program);
return;
}
static void log_callback(void* ptr, int level, const char* fmt, va_list vl)
{
vfprintf(stdout, fmt, vl);
}
/*
* audio renderer code (oss)
*/
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/soundcard.h>
#define OSS_DEVICE "/dev/dsp0"
struct audio_dsp
{
int audio_fd;
int channels;
int format;
int speed;
};
int map_formats(enum AVSampleFormat format)
{
switch(format)
{
case AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8:
return AFMT_U8;
case AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16:
return AFMT_S16_LE;
default:
return AFMT_U8;
}
}
int set_audio(struct audio_dsp* dsp)
{
if (dsp->audio_fd == -1)
{
printf("Invalid audio dsp id!\n");
return -1;
}
if (-1 == ioctl(dsp->audio_fd, SNDCTL_DSP_SETFMT, &dsp->format))
{
printf("Failed to set dsp format!\n");
return -1;
}
if (-1 == ioctl(dsp->audio_fd, SNDCTL_DSP_CHANNELS, &dsp->channels))
{
printf("Failed to set dsp format!\n");
return -1;
}
if (-1 == ioctl(dsp->audio_fd, SNDCTL_DSP_SPEED, &dsp->speed))
{
printf("Failed to set dsp format!\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int play_pcm(struct audio_dsp* dsp, unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
if (dsp->audio_fd == -1)
{
printf("Invalid audio dsp id!\n");
return -1;
}
if (-1 == write(dsp->audio_fd, buf, size))
{
printf("Failed to write audio dsp!\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/* audio renderer code end */
/* video renderer code*/
#include <linux/fb.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#define FB_DEVICE "/dev/fb0"
enum pic_format
{
eYUV_420_Planer,
};
struct video_fb
{
int video_fd;
struct fb_var_screeninfo vinfo;
struct fb_fix_screeninfo finfo;
unsigned char *fbp;
AVFrame *frameRGB;
struct
{
int x;
int y;
} video_pos;
};
int open_video(struct video_fb *fb, int x, int y)
{
int screensize;
fb->video_fd = open(FB_DEVICE, O_WRONLY);
if (fb->video_fd == -1) return -1;
if (ioctl(fb->video_fd, FBIOGET_FSCREENINFO, &fb->finfo)) return -2;
if (ioctl(fb->video_fd, FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO, &fb->vinfo)) return -2;
printf("video device: resolution %dx%d, %dbpp\n", fb->vinfo.xres, fb->vinfo.yres, fb->vinfo.bits_per_pixel);
screensize = fb->vinfo.xres * fb->vinfo.yres * fb->vinfo.bits_per_pixel / 8;
fb->fbp = (unsigned char *) mmap(0, screensize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fb->video_fd, 0);
if (fb->fbp == -1) return -3;
if (x >= fb->vinfo.xres || y >= fb->vinfo.yres)
{
return -4;
}
else
{
fb->video_pos.x = x;
fb->video_pos.y = y;
}
fb->frameRGB = avcodec_alloc_frame();
if (!fb->frameRGB) return -5;
return 0;
}
/* only 420P supported now */
int show_picture(struct video_fb *fb, AVFrame *frame, int width, int height, enum pic_format format)
{
struct SwsContext *sws;
int i;
unsigned char *dest;
unsigned char *src;
if (fb->video_fd == -1) return -1;
if ((fb->video_pos.x >= fb->vinfo.xres) || (fb->video_pos.y >= fb->vinfo.yres)) return -2;
if (fb->video_pos.x + width > fb->vinfo.xres)
{
width = fb->vinfo.xres - fb->video_pos.x;
}
if (fb->video_pos.y + height > fb->vinfo.yres)
{
height = fb->vinfo.yres - fb->video_pos.y;
}
if (format == PIX_FMT_YUV420P)
{
sws = sws_getContext(width, height, format, width, height, PIX_FMT_RGB32, SWS_FAST_BILINEAR, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (sws == 0)
{
return -3;
}
if (sws_scale(sws, frame->data, frame->linesize, 0, height, fb->frameRGB->data, fb->frameRGB->linesize))
{
return -3;
}
dest = fb->fbp + (fb->video_pos.x+fb->vinfo.xoffset) * (fb->vinfo.bits_per_pixel/8) +(fb->video_pos.y+fb->vinfo.yoffset) * fb->finfo.line_length;
for (i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
memcpy(dest, src, width*4);
src += fb->frameRGB->linesize[0];
dest += fb->finfo.line_length;
}
}
return 0;
}
void close_video(struct video_fb *fb)
{
if (fb->video_fd != -1)
{
munmap(fb->fbp, fb->vinfo.xres * fb->vinfo.yres * fb->vinfo.bits_per_pixel / 8);
close(fb->video_fd);
fb->video_fd = -1;
}
}
/* video renderer code end */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
AVFormatContext* pCtx = 0;
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = 0;
AVCodec *pCodec = 0;
AVPacket packet;
AVFrame *pFrame = 0;
FILE *fpo1 = NULL;
FILE *fpo2 = NULL;
int nframe;
int err;
int got_picture;
int picwidth, picheight, linesize;
unsigned char *pBuf;
int i;
int64_t timestamp;
struct options opt;
int usefo = 0;
struct audio_dsp dsp;
struct video_fb fb;
int dusecs;
float usecs1 = 0;
float usecs2 = 0;
struct timeval elapsed1, elapsed2;
int decoded = 0;
av_register_all();
av_log_set_callback(log_callback);
av_log_set_level(50);
if (parse_options(&opt, argc, argv) < 0 || (strlen(opt.finput) == 0))
{
show_help(argv[0]);
return 0;
}
err = avformat_open_input(&pCtx, opt.finput, 0, 0);
if (err < 0)
{
printf("\n->(avformat_open_input)\tERROR:\t%d\n", err);
goto fail;
}
err = avformat_find_stream_info(pCtx, 0);
if (err < 0)
{
printf("\n->(avformat_find_stream_info)\tERROR:\t%d\n", err);
goto fail;
}
if (opt.streamId < 0)
{
av_dump_format(pCtx, 0, pCtx->filename, 0);
goto fail;
}
else
{
printf("\n extra data in Stream %d (%dB):", opt.streamId, pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->extradata_size);
for (i = 0; i < pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->extradata_size; i++)
{
if (i%16 == 0) printf("\n");
printf("%2x ", pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->extradata[i]);
}
}
/* try opening output files */
if (strlen(opt.foutput1) && strlen(opt.foutput2))
{
fpo1 = fopen(opt.foutput1, "wb");
fpo2 = fopen(opt.foutput2, "wb");
if (!fpo1 || !fpo2)
{
printf("\n->error opening output files\n");
goto fail;
}
usefo = 1;
}
else
{
usefo = 0;
}
if (opt.streamId >= pCtx->nb_streams)
{
printf("\n->StreamId\tERROR\n");
goto fail;
}
if (opt.lstart > 0)
{
err = av_seek_frame(pCtx, opt.streamId, opt.lstart, AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY);
if (err < 0)
{
printf("\n->(av_seek_frame)\tERROR:\t%d\n", err);
goto fail;
}
}
/* for decoder configuration */
if (!opt.nodec)
{
/* prepare codec */
pCodecCtx = pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec;
if (opt.thread_count <= 16 && opt.thread_count > 0 )
{
pCodecCtx->thread_count = opt.thread_count;
pCodecCtx->thread_type = FF_THREAD_FRAME;
}
pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
if (!pCodec)
{
printf("\n->can not find codec!\n");
goto fail;
}
err = avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, 0);
if (err < 0)
{
printf("\n->(avcodec_open)\tERROR:\t%d\n", err);
goto fail;
}
pFrame = avcodec_alloc_frame();
/* prepare device */
if (opt.bplay)
{
/* audio devices */
dsp.audio_fd = open(OSS_DEVICE, O_WRONLY);
if (dsp.audio_fd == -1)
{
printf("\n-> can not open audio device\n");
goto fail;
}
dsp.channels = pCodecCtx->channels;
dsp.speed = pCodecCtx->sample_rate;
dsp.format = map_formats(pCodecCtx->sample_fmt);
if (set_audio(&dsp) < 0)
{
printf("\n-> can not set audio device\n");
goto fail;
}
/* video devices */
if (open_video(&fb, 0, 0) != 0)
{
printf("\n-> can not open video device\n");
goto fail;
}
}
}
nframe = 0;
while(nframe < opt.frames || opt.frames == -1)
{
gettimeofday(&elapsed1, NULL);
err = av_read_frame(pCtx, &packet);
if (err < 0)
{
printf("\n->(av_read_frame)\tERROR:\t%d\n", err);
break;
}
gettimeofday(&elapsed2, NULL);
dusecs = (elapsed2.tv_sec - elapsed1.tv_sec)*1000000 + (elapsed2.tv_usec - elapsed1.tv_usec);
usecs2 += dusecs;
timestamp = av_rescale_q(packet.dts, pCtx->streams[packet.stream_index]->time_base, (AVRational){1, AV_TIME_BASE});
printf("\nFrame No %5d stream#%d\tsize %6dB, timestamp:%6lld, dts:%6lld, pts:%6lld, ", nframe++, packet.stream_index, packet.size,
timestamp, packet.dts, packet.pts);
if (packet.stream_index == opt.streamId)
{
#if 0
for (i = 0; i < 16; /*packet.size;*/ i++)
{
if (i%16 == 0) printf("\n pktdata: ");
printf("%2x ", packet.data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
#endif
if (usefo)
{
fwrite(packet.data, packet.size, 1, fpo1);
fflush(fpo1);
}
if (pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO && !opt.nodec)
{
picheight = pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->height;
picwidth = pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->width;
gettimeofday(&elapsed1, NULL);
avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &got_picture, &packet);
decoded++;
gettimeofday(&elapsed2, NULL);
dusecs = (elapsed2.tv_sec - elapsed1.tv_sec)*1000000 + (elapsed2.tv_usec - elapsed1.tv_usec);
usecs1 += dusecs;
if (got_picture)
{
printf("[Video: type %d, ref %d, pts %lld, pkt_pts %lld, pkt_dts %lld]",
pFrame->pict_type, pFrame->reference, pFrame->pts, pFrame->pkt_pts, pFrame->pkt_dts);
if (pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->pix_fmt == PIX_FMT_YUV420P)
{
if (usefo)
{
linesize = pFrame->linesize[0];
pBuf = pFrame->data[0];
for (i = 0; i < picheight; i++)
{
fwrite(pBuf, picwidth, 1, fpo2);
pBuf += linesize;
}
linesize = pFrame->linesize[1];
pBuf = pFrame->data[1];
for (i = 0; i < picheight/2; i++)
{
fwrite(pBuf, picwidth/2, 1, fpo2);
pBuf += linesize;
}
linesize = pFrame->linesize[2];
pBuf = pFrame->data[2];
for (i = 0; i < picheight/2; i++)
{
fwrite(pBuf, picwidth/2, 1, fpo2);
pBuf += linesize;
}
fflush(fpo2);
}
if (opt.bplay)
{
/* show picture */
show_picture(&fb, pFrame, picheight, picwidth, PIX_FMT_YUV420P);
}
}
}
av_free_packet(&packet);
}
else if (pCtx->streams[opt.streamId]->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO && !opt.nodec)
{
int got;
gettimeofday(&elapsed1, NULL);
avcodec_decode_audio4(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &got, &packet);
decoded++;
gettimeofday(&elapsed2, NULL);
dusecs = (elapsed2.tv_sec - elapsed1.tv_sec)*1000000 + (elapsed2.tv_usec - elapsed1.tv_usec);
usecs1 += dusecs;
if (got)
{
printf("[Audio: %5dB raw data, decoding time: %d]", pFrame->linesize[0], dusecs);
if (usefo)
{
fwrite(pFrame->data[0], pFrame->linesize[0], 1, fpo2);
fflush(fpo2);
}
if (opt.bplay)
{
play_pcm(&dsp, pFrame->data[0], pFrame->linesize[0]);
}
}
}
}
}
if (!opt.nodec && pCodecCtx)
{
avcodec_close(pCodecCtx);
}
printf("\n%d frames parsed, average %.2f us per frame\n", nframe, usecs2/nframe);
printf("%d frames decoded, average %.2f us per frame\n", decoded, usecs1/decoded);
fail:
if (pCtx)
{
avformat_close_input(&pCtx);
}
if (fpo1)
{
fclose(fpo1);
}
if (fpo2)
{
fclose(fpo2);
}
if (!pFrame)
{
av_free(pFrame);
}
if (!usefo && (dsp.audio_fd != -1))
{
close(dsp.audio_fd);
}
if (!usefo && (fb.video_fd != -1))
{
close_video(&fb);
}
return 0;
}